各个流程的处理过程大同小异
GATK PON
A Panel of Normal or PON is a type of resource used in somatic variant analysis. Depending on the type of variant you’re looking for, the PON will be generated differently. What all PONs have in common is that :
- they are made from normal samples (in this context, $\color{red}{“normal”}$ means derived from healthy tissue that is believed to not have any somatic alterations)
- their main purpose is to capture recurrent technical artifacts in order to improve the results of the variant calling analysis.
As a result, the most important selection criteria for choosing normals to include in any PON are the technical properties of how the data was generated. It’s very important to use normals that are as technically similar as possible to the tumor (same exome or genome preparation methods, sequencing technology and so on). Additionally, the samples should come from subjects that were young and healthy to minimize the chance of using as normal a sample from someone who has an undiagnosed tumor. Normals are typically derived from blood samples.
There is no definitive rule for how many samples should be used to make a PON (even a small PON is better than no PON) but in practice we recommend aiming for a minimum of 40.
At the Broad Institute, we typically make a standard PON for a given version of the pipeline (corresponding to the combination of all protocols used in production to generate the sequence data, starting from sample preparation and including the analysis software) and use it to process all tumor samples that go through that version of the pipeline. Because we process many samples in the same way, we are able to make PONs composed of hundreds of samples.
MSK
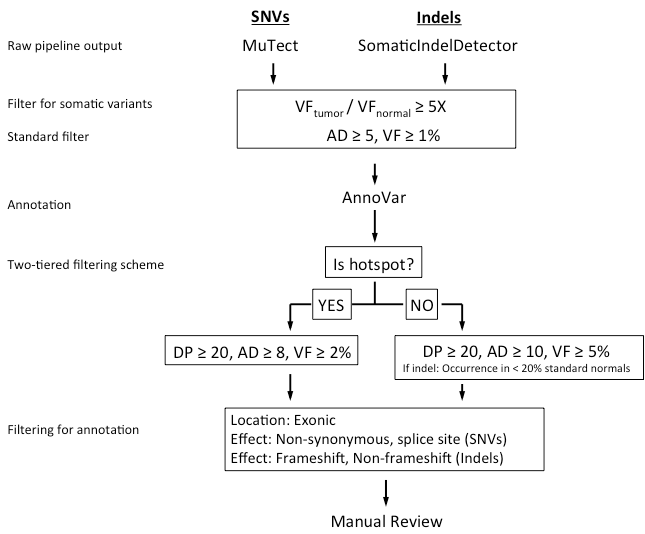
Filtering for high confidence mutations: Raw SNV and indel calls are subjected to a series of filtering steps to ensure only high-confidence calls are admitted to the final step of manual review. These parameters include
- (1) evidence of it being a somatic mutation (i.e., ratio between mutation frequencies in the tumor and normal samples to be ≥ 5.0);
- (2) whether the mutation is a known hotspot mutation (refer to Appendix 1a for details);
- (3) reference on in house ‘standard normal’ based on common artifacts;
- (4) technical characteristics that use coverage depth (DP), number of mutant reads (AD), mutation frequency (VF).
The filtering scheme and threshold are shown in Figure 1 below. The threshold values for the filtering criteria were established based on paired-sample mutation analysis on replicates of normal FFPE samples, and optimized to reject all false positive SNVs and almost all false positive indel calls from the reference dataset.