他们是怎么做的?
目前已经发表的一些体系检测软件,引用了一些检测方法,为我们提供了参考。主要有3个相对比较主流的方案:
- 从体系检测结果中减去胚系检出结果
- 体细胞变异调用者使用贝叶斯方法
- Fisher精确统计方法
Fisher 检验(目前产品在用)
参考文献
[1] Hansen N F , Gartner J J , Lan M , et al. Shimmer: detection of genetic alterations in tumors using next-generation sequence data.[J]. Bioinformatics, 2013(12):1498-1503.
[2] Koboldt D C , Zhang Q , Larson D E , et al. VarScan 2: Somatic mutation and copy number alteration discovery in cancer by exome sequencing[J]. Genome Research, 2012, 22(3):568-576.
介绍
以Varscan为例,基于Fisher检验是否存在显著性(Pvalue < 0.1) ,及双端情况将数据划分为3类(LOH、Germline、Somatic)。
补充说明
因为目前监测体系变异检测,会涉及到一些低频检测需求(1%甚至更低的频率检测需求),在临床使用中,发现一个难以避免的问题,会存在由于对照深度不足导致的P值永远难以显著(即使对照纯阴性也无法存在显著性差异)。模拟统计计算如下:
组织深度1200x; 对照纯阴性。(对照阈值300x)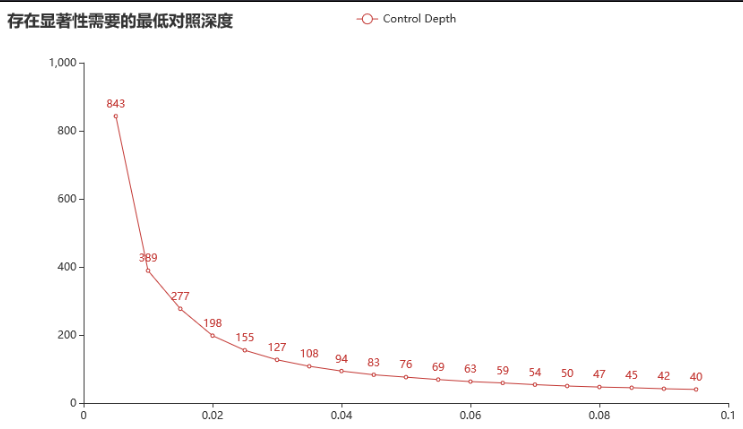
对于检测限 1% 的突变(组织/血浆测序深度1200x时),对照只有达到 389x 以上时,才可能有显著性。
对于一个 3% 的突变(组织/血浆测序深度1200x时),对照只有达到 127x 以上时,才可能有显著性。
对于一个 0.5% 的突变(组织/血浆测序深度1200x时),对照只有达到 843x 以上时,才可能有显著性。
WES产品 500x;对照纯阴性。(对照阈值200x)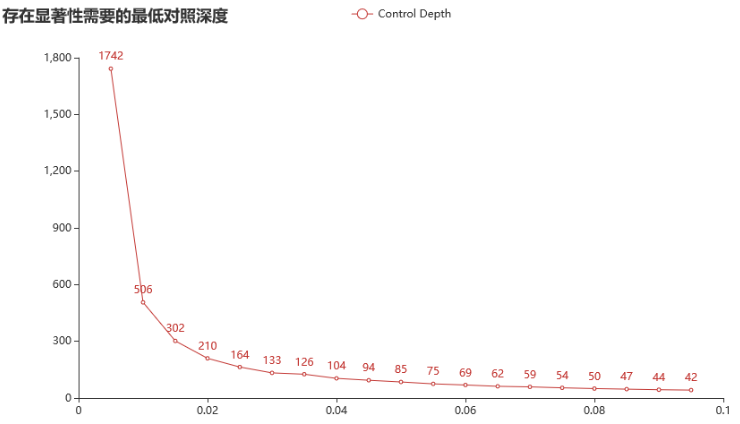
针对检测限 3% 的突变,纯阴对照需要达到 133x 才能存在显著性。
针对一个 1% 的突变,纯阴对照需要达到 506x 才能存在显著性。
做减法
参考文献
[1] A comparative analysis of algorithms for somatic SNV detection in cancer.[J]. Bioinformatics, 2013.
[2] GATK mutect2
介绍
以GATK为例
A variant allele in the case sample is not called if the site is variant in controls.
We explain an exception for GATK4 Mutect2 in a bit.
Historically, somatic callers have called somatic variants at the site-level. That is, if a variant site in the case is also variant in the matched control or in a population resource, e.g. dbSNP, even if the variant allele is different than the control or resource it is discounted from the somatic callset. This practice stems in part from cancer study designs where the control normal sample is sequenced at much lower depth than the case tumor sample. Because of the assumption mutations strike randomly, cancer geneticists view mutations at sites of common germline variation with skepticism. Remember for humans, common germline variant sites occur roughly on average one in a thousand reference bases. So if a commonly variant site accrues additional mutations, we must weigh the chance of it having arisen from a true somatic event or it being something else that will likely not add value to downstream analyses. For most sites and typical analyses, the latter is the case. The variant is unlikely to have arisen from a somatic event and more likely to be some artifact or germline variant, e.g. from mapping or cross-sample contamination.
GATK4 Mutect2 still applies this practice in part. The tool discounts variant sites shared with the panel of normals or with a matched normal control’s unambiguously variant site. If the matched normal’s variant allele is supported by few reads, at low allele fraction, then the tool accounts for the possibility of the site not being a germline variant.
When it comes to the population germline resource, GATK4 Mutect2 distinguishes between the variant alleles in the germline resource and the case sample. That is, Mutect2 will call a variant site somatic if the allele differs from that in the germline resource.
[1] A comparative analysis of algorithms for somatic SNV detection in cancer.[J]. Bioinformatics, 2013.
[2] GATK mutect2
体细胞变异调用者使用贝叶斯方法
参考文献
[1] Cibulskis K , Lawrence M S , Carter S L , et al. Sensitive detection of somatic point mutations in impure and heterogeneous cancer samples[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(3):213-219.
[2] Christopher, T, Saunders, et al. Strelka: accurate somatic small-variant calling from sequenced tumor-normal sample pairs.[J]. Bioinformatics, 2012.
[3] Yuichi S , Yusuke S , Kenichi C , et al. An empirical Bayesian framework for somatic mutation detection from cancer genome sequencing data[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2013(7):e89-e89.
[4] SomaticSniper[J]. Bioinformatics, 2012.
[5] Identification of somatic mutations in cancer through Bayesian-based analysis of sequenced genome pairs[J]. Bmc Genomics, 2013, 14.