Methods
核心分析流程共分为4个步骤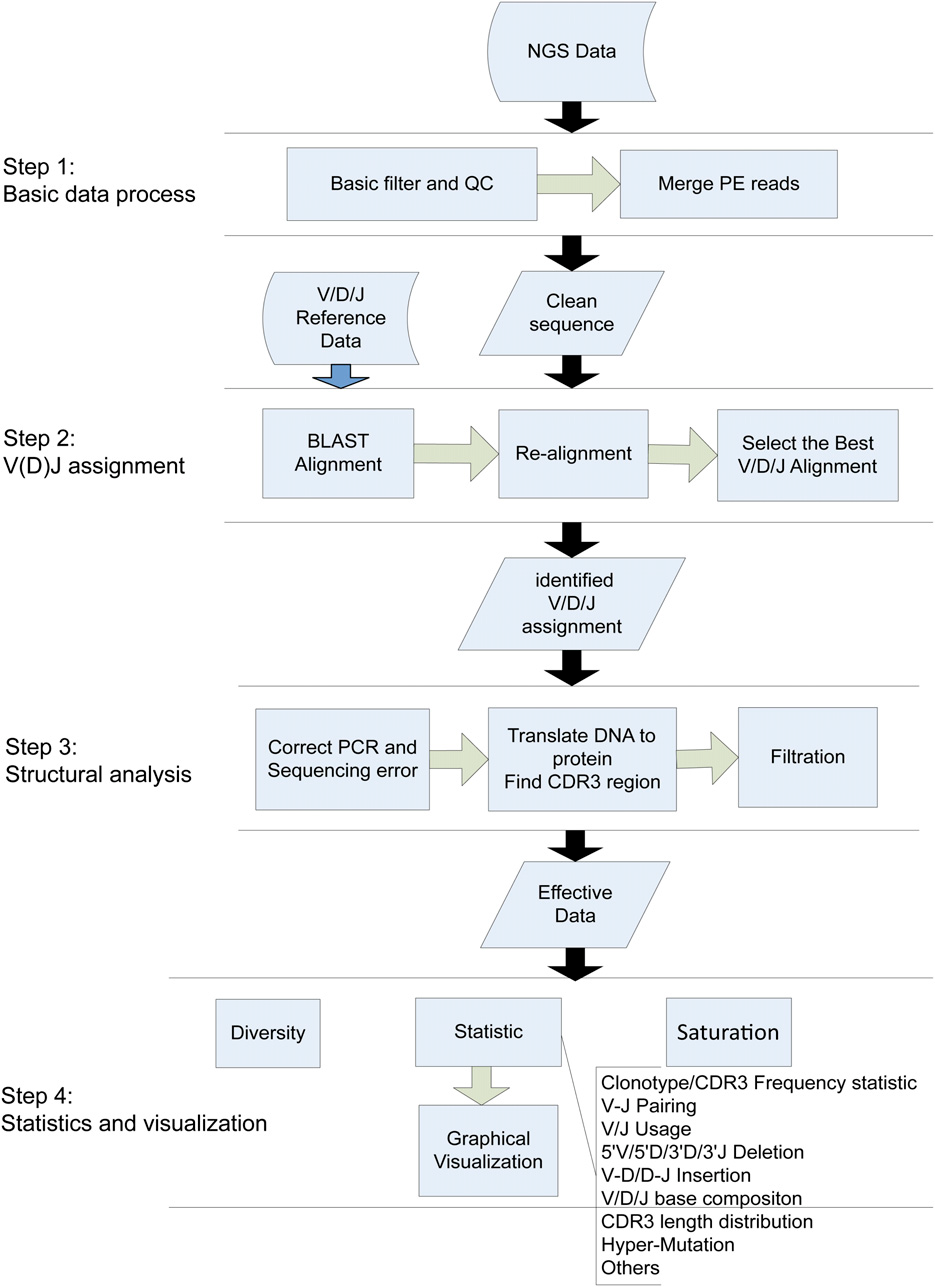
basic data processing
In the first step, the readswere checked for inclusion of adaptorsequences. If any adaptor sequence was detected and locatedwithin 50 bp of the 39end of the read, it was deleted from theread. Reads bearing adaptor sequence at the 59 end or .5%“N” bases were discarded. The average base quality of eachreadwas calculated after removing the low-quality bases (basequality,10) at the 39 end. Further filtration left out reads withaverage quality ,15. For Illumina paired-end (PE) sequencing,the PE reads were merged at their overlapping region. ForPE readswith insertion length longer than the length of a singleread, the COPE (Liu et al. 2012) toolwas used; otherwise readswere assembled by an in-house program. Themain parametersfor both tools included themaximumoverlapping length (readlength), minimum overlapping length (10 bp), mismatch rate(10%) at the overlapping region, and ratio
V(D)J assignment
The V/D/J reference sequences were downloaded from the IMGT database, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system (http://www.imgt.org/). Processed sequences were aligned to the V, (D), J references, respectively, by BLAST (Altschul et al. 1990; Zhang et al. 2000; Ye et al. 2006) and specific parameters were applied to accommodate the differences in lengths of V, (D), J segments (BLAST parameters: V, -W 15 -K 3 -v 1 -b 3; D, -W 4 -K 3 -v 3 -b 5; and J, -W 10 -K 3 -v 1 -b 3). The high similarity among the genes and alleles of the germline sequences, along with the diversity of V/D/J gene rearrangement, gave rise to difficulties for accurate alignment. This might eventually lead to an incorrect structural analysis (CDR3 identification, deletion, or insertion). To improve the accuracy, a second alignment procedure was developed to identify exactly the V/D/J genes (Figure 2). First, a global alignment strategy, which attempted to align every base in every sequence, was used for the non-CDR3 region of the sequence. The mapped region generated from BLAST became a new seed and served as starting points for bootstrapping (base-by-base) extension to both directions, until the entire non-CDR3 region in the query was mapped to the target (reference) sequence. The mapping score was calculated according to these rules: reward for a nucleotide match was 5 and penalty for a nucleotide mismatch was 24. Second, the M-mismatch extension model of local alignment strategy was applied to locate the exact end positions of V and J genes during CDR3 region realignment. The procedure began at the CDR3 start position in the V gene or the CDR3 end position in the J gene and continuously extended in one direction until the preset mismatch limit was reached, generating the longest possible interval with the highest score. The mismatch numbers allowed for V/D/J genes were determined based on the analysis result of publicly available rearrangement sequences (http://www.imgt.org/ligmdb/) (Supporting Information, Figure S2A) and adjusted accordingly for different TCR and BCR chains (mismatches allowed: TRBV/J, TRAV/J, 0; IGHV/J, 2; IGKV/J, IGLV/J, 7). As shown in Figure S2A, these mismatch limits took mutations into consideration and covered .99.5% of all defined rearrangement sequences. Because the entire D gene was located within the CDR3 region, only the M-mismatch extension model was used for its realignment (mismatches allowed: TRBD, 0; IGHD, 4). Finally, all data including alignment score, identity, mismatch number, and alignment length were processed, and the alignment with highest score and identity larger than the threshold (.80%) was selected as the best hit. However, there might be several best hits with the same score due to the homology among the germline genes and alleles. In this case, the reference with the fewest deletions was selected, as shorter deletions are more likely to happen according to previous reported results (Warren et al. 2009) and our analysis from actual public rearrangement data (Figure S2B).